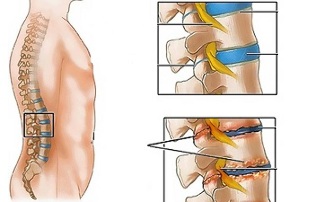
Lumbar fibroids are a chronic disease that develops as a result of degenerative-dystrophy in the intervertebral discs. The disease is common and affects most people between the ages of 25 and 40.
According to statistics, adults experience back pain at least once in their lifetime, while 95% of cases are due to degenerative spine.
Patients with advanced lumbar necrosis, persistent pain and other manifestations are considered to be temporarily disabled. If their condition does not improve within four months, the matter of forming a disability group will be decided.
Lumbar spinal tumor disease is a serious medical and social problem, as the disease mainly affects people of working age and in addition, if left untreated, it can cause formationdisc herniation.
Causes and Risk Factors
Factors that lead to the development of lumbar necrosis are:
- structural anomalies in the spine;
- paralysis - congenital pathology of the spine, characterized by detachment of the first vertebra from the sacrum and its transformation into the sixth lumbar (complementary);
- sacral is a congenital condition in which the fifth lumbar vertebra fuses with the sacrum;
- asymmetric arrangement of the joint cavities of the disc joint;
- pathological stenosis;
- reflects pain caused by the spine (somatic and muscle);
- obesity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- long exposure to vibration;
- systematic physical stress; Smoking
- .
Unfavorable static-dynamic load associated with one or several risk factors leading to a change in the physiological properties of the spinal core of the fibrous disc, has the role of absorbing impulse and ensuringmobility of the spine. This process is based on the polymerization of polysaccharide, which leads to the loss of moisture in the tissue of the colloidal core. As a result, the marrow nuclei, and with it the fibrous discs, lose their elastic properties. Further mechanical stress causes the protrusion of the annular fibers to lose their elasticity. This phenomenon is called concave convex phenomenon. Cracks appear in the fibrous nucleus, through which the fibrous kernel fragments fall out (prolapse, disc herniation).
Prolonged compression of nerve roots within some intra-abdominal organs over time leads to impaired function.
Spinal fragment instability is accompanied by reactive changes in the body of the neighboring vertebrae, the disc joints and the simultaneous development of spondylolisthesis. Significant muscle contraction, for example, based on the background of physical activity, leads to displacement of the vertebral body and entrapping of the nerve root with the development of lens syndrome.
Another cause of pain and nerve symptoms in lumbar degenerative disease can be osteoporosis - the growth of bones on vertebral body and processes causing lens syndrome orpathology of the marrow (spinal cord compression).
Types of diseases
Depending on which structure is involved in the pathological process, lumbar osteonecrosis is clinically manifested by the following syndromes:
- reflex- hemiplegia, migraine, low back pain; development on the basis of excessive reflexes of the back muscles;
- compression (spine, blood vessel, lens)- compression (compression) of the spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots leading to their development. Examples are nuclear gland inflammation, ischemia.
Symptoms of lumbar necrosis
In lumbar necrosis, symptoms are determined by which structures are involved in the pathological process.
Low back pain occurs with hypothermia or physical stress, and sometimes for no apparent reason. The pain appeared suddenly and was of a shooting nature. It intensifies when sneezing, coughing, rotating, exercising, sitting, standing, walking. In the tummy position, the sensation of pain is significantly weaker. Sensitivity and reflexes are preserved, range of motion of the lumbar spine is reduced.
Look to the touch:
- soreness in the lumbar region;
- spasms of the spinal muscles;
- smooths lumbar curvatures, in many cases associated with scoliosis.
Lumbar nerve root syndrome is negative. When the legs are straightened, the patient noted an increased pain sensation in the lumbar region, not pain in the lower extremities.
Usually, with lumbar necrosis, pain recurs, each pain is more intense and prolonged.
In low back pain, the clinical picture resembles lower back pain, but an increase in pain intensity occurs over a few days.
In migraine, the patient complains of pain in the lumbar region spreading to one or both lower extremities. The pain spread to the buttocks and back of the thighs and never to the legs.
Chiropractors are characterized by vasomotor disorders:
- changes in temperature and skin color of the lower extremities;
- feels hot or cold;
- violation of blood circulation.
The development of lumbar compression syndrome is clinically manifested by the following symptoms:
- decreased skin potassium;
- shooting;
- weakens or completely loses a deep reflex;
- peripheral paralysis.
With squeezing syndrome, pain is exacerbated by bending trunks, sneezing, and coughing.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of lumbar necrosis is done on the database of the clinical picture of the disease, laboratory research methods and instruments.
Blood test based on lumbar necrosis:
- decreases calcium concentration;
- increases ESR;
- increases the level of alkaline phosphatase.
In the diagnosis of lumbar tumors, the X-ray examination of the spine is very important.
Prolonged compression of nerve roots within some intra-abdominal organs over time leads to impaired function.
The diagnostic X-ray signs that confirm the diagnosis are:
- changes the configuration of the affected segment;
- pseudospondylolisthesis (displacement of adjacent vertebral bodies);
- deformation of closed plates;
- flattens the disc;
- unequal height of the disc (a symptom of a disc), associated with asymmetric muscle tone.
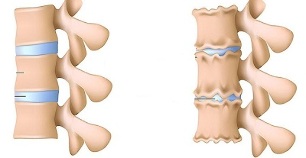
Also in the diagnosis of lumbar necrosis, if indicated, used:
- myelogram, computation or magnetic resonance imaging - essential for persistent symptoms, the development of neurological deficiency;
- scans (the study of phosphorus accumulation in the skeletal system, labeled tech-99) - is done if a tumor or infection or spinal injury is suspected.
The differential diagnosis of lumbar tumors is made with the following diseases:
- spondylolisthesis;
- degenerative cervical vertebrae disease;
- ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
- infectious process (disc inflammation, spinal inflammation);
- cancerous processes (primary tumor of the spine or other metastatic lesions);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- degenerative deformity of the hip joint;
- reflects pain (disease of internal organs and large blood vessels).
Treatment of lumbar necrosis
For lumbar necrosis, the following treatment strategies are commonly followed:
- resting in bed for 2-3 days; Traction force
- of the spinal segment is affected;
- strengthens the back and abdominal muscles (creating the so-called muscle corset);
- affects the pathological processes of musculoskeletal and neuromuscular diseases.
Low back pain occurs with hypothermia or physical stress, and sometimes for no apparent reason.
In most cases, conservative treatment of lumbar necrosis is carried out, including the following measures:
- infiltrates the muscles with local anesthetic solution;
- take a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug;
- used a desensitizer;
- vitamin therapy;
- take sedatives and antidepressants;
- manual therapy, massage;
- physical therapy exercises;
- acupuncture;
- relax after isotope.
The absolute indications for the surgical treatment of lumbar tumors are:
- acute or subacute spinal cord compression;
- develops cauda equina syndrome, characterized by dysfunction of the pelvic organs, sensory and motor disorders.
Therapeutic exercises for lumbar necrosis
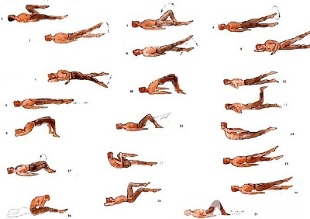
Physiotherapy plays an important role in the complex treatment of lumbar necrosis. Regular exercises allow you to normalize the muscle tone of the vertebral muscles, improve the metabolism in the tissues affected by the pathological process and in addition, form a muscular braGood development can support the spine in the correct position, removing unnecessary static loads from it.
For the most effective lumbar osteoarthritis exercises, you need to follow these principles:
- regularity of classes;
- gradually increases the intensity of physical activity;
- avoid overwork during school hours.
Physiotherapy should be performed under the guidance of an experienced guide who will choose the exercises that are most effective for a particular patient and control the correctness of their execution. .
According to statistics, adults experience back pain at least once in their lifetime, while 95% of cases are due to spinal degeneration.
In addition to classes with instructors, you should do a series of morning exercises every day, including special exercises for lumbar necrosis.
- Relax and contract your abdominal muscles.The starting position is to stand, with feet shoulder-width apart, hands lower. Breathe in gently, relaxing the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. While exhaling, pull in as far as you can, straining your abdominal muscles. Exercise should be repeated until mild fatigue occurs.
- Head movements accompanying spinal flexion.The starting position is kneeling, leaning on the floor, arms outstretched, back straight. Slowly raise your head and bend your back. Hold in this position for a few seconds, and then return to the starting position gently. Repeat at least 10-12 times.
- "Pendulum".The posture begins to lie on your back, hands along the body, legs bent at right angles to the knee and hip joints. Rotate feet right and left in a swinging pendulum, trying to touch the floor. In this case, the shoulder blade cannot be torn off the floor. Boat
- .Start in a prone position, arms stretched forward. Tear the upper body and legs off the floor, bending in the back. Hold this position for 5-6 seconds and slowly return to the starting position. Run 10 times.
Potential consequences and complications
The main complications of lumbar necrosis are:
- forms a herniated disc;
- vegetative muscle dystonia;
- spondylolisthesis, spondylolisthesis;
- bone formation;
- degenerative vertebrae;
- narrows the spinal canal, leading to compression of the spinal cord and can cause permanent disability and loss of quality of life.
Prolonged compression of nerve roots within some intra-abdominal organs over time leads to impaired function. As a result, the patient suffers from bowel dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea, flatulence) and pelvic organs (urination disorders, erectile dysfunction, apathy, infertility).
Forecast
Pain syndrome in lumbar necrosis occurs in the form of remission and paroxysmal. Low back pain lasted for 10-15 days, after which the patient's condition improved, and the pain subsided. A favorable outcome can be prevented by related secondary diseases. Usually, with lumbar necrosis, the pain recurs, each pain more intense and lasting.
Physiotherapy plays an important role in the complex treatment of lumbar necrosis.
Patients with advanced lumbar necrosis, persistent pain and other manifestations are considered to be temporarily disabled. If their condition does not improve within four months, the matter of forming a disability group will be decided.
Precautions
Prevent the development of osteonecrosis of the spine includes the following measures:
- quit smoking;
- normalizes body weight;
- improves general fitness, active lifestyle;
- avoids provocative conditions (weight lifting, sudden movement, turning, bending).












































